IGBC Certification is evolving in large-scale architecture projects to minimize the negative impact on the environment. Each sqft to sqyd is associated with a magical commercial number. IGBC Certification urges to address national priorities like energy efficiency, water efficiency, reduction in fossil fuels, waste management, and conservation of national resources.
Under IGBC certification, the New Green Building Rating System enables architects to apply measurable green concepts and techniques. Despite concerns about the suitability of green building rating systems in India, focusing on sustainable development in design and operation remains crucial.
Adopting a green approach to architectural planning and design is essential to reduce environmental impact and mitigate sick building syndrome. As a result, please find a simplified summary of the IGBC certification process and the seven key sustainability criteria for your projects. This toolkit also features IGBC (Indian Green Building Council) credentials, fee structure, and certification process.
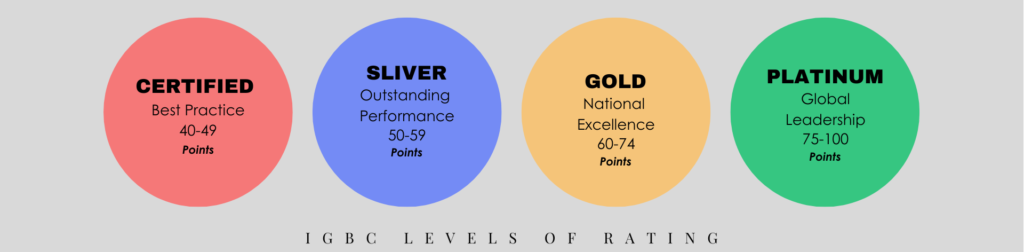
Levels of Rating
Each criterion contains mandatory and credit-based requirements that increase a project’s certification level and recognition. The different levels of rating are awarded based on the points earned. Furthermore, every new green building project should meet mandatory requirements. The following outlines the criteria for levels of rating:
Seven Criteria Checklist for IGBC Certification
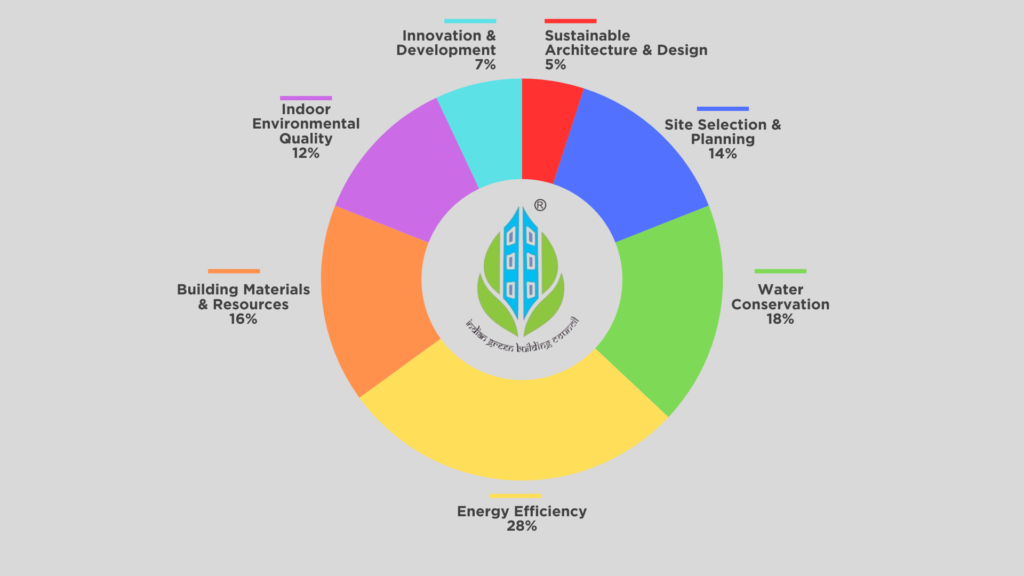
1. Sustainable Architecture and Design (SA): 5%
A plot of land with herbs, shrubs, and other living organisms is integral to our ecosystem. To ensure site preservation and integrated design, this particular criterion consists of three credit requirements. They are:
| Module | Points | |||
| Owner-Occupied Building | Tenant-Occupied Building | |||
| Sustainable Architecture and Design (SA) | 5 | 5 | ||
| SA Credit 1 | Integrated Design Approach | 1 | 1 | |
| SA Credit 2 | Site Preservation | 2 | 2 | |
| SA Credit 3 | Passive Architecture | 2 | 2 | |
Certification Compliance Requirements:
- Ensure that the project involves team members from multi-disciplinary fields and at least document three of the meetings.
- Demonstrate that the project partially preserves one of the site features like waterbodies, rock, contour, and others.
- Adopt passive design measures using a measurable simulation approach.
2. Site Selection and Planning (SSP): 14%
When selecting a site for infrastructure development, it is a high priority to promote sustainability. This criterion focuses on reducing the site’s ecological footprint and optimizing the building to seamlessly blend with the environment. The requirements are:
| Module | Points | |||
| Owner-Occupied Building | Tenant-Occupied Building | |||
| Site Selection and Planning (SSP) | 14 | 14 | ||
| SSP Mandatory 1 | Local Building Regulations | R | R | |
| SSP Mandatory 2 | Soil Erosion Control | R | R | |
| SSP Credit 1 | Basic Amenities | 1 | 1 | |
| SSP Credit 2 | Proximity to Public Transport | 1 | 1 | |
| SSP Credit 3 | Low-emitting Vehicles | 1 | 1 | |
| SSP Credit 4 | Natural Topography or Vegetation | 2 | 2 | |
| SSP Credit 5 | Preservation or Transplantation of Trees | 1 | 1 | |
| SSP Credit 6 | Heat Island Reduction, Non-roof | 2 | 2 | |
| SSP Credit 7 | Heat Island Reduction, Roof | 2 | 2 | |
| SSP Credit 8 | Outdoor Light Pollution Reduction | 1 | 1 | |
| SSP Credit 9 | Universal Design | 1 | 1 | |
| SSP Credit 10 | Basic Facilities for Construction Workforce | 1 | 1 | |
| SSP Credit 11 | Green Building Guidelines | 1 | 1 | |
Certification Compliance Requirements:
- Execute approved site/building plans for construction.
- Submit an environmental clearance certificate if the built-up area is >20,000 sqm.
- Take soil erosion measures before, during, and after construction.
3. Water Conservation (WC): 18%
The trend of water resources has shifted from being abundant and free to costing around 20 INR per liter. Climate change and extensive deforestation have caused reduced rainfall in most parts of India. To mitigate the impact on potable water consumption and recharge the groundwater table, it is essential to implement water conservation measures. Water conservation requirements include:
| Module | Points | |||
| Owner-Occupied Building | Tenant-Occupied Building | |||
| Water Conservation(WC) | 18 | 19 | ||
| WC Mandatory Requirement 1 | Rainwater Harvesting, Roof & Non-roof | R | R | |
| WC Mandatory Requirement 2 | Water-Efficient Plumbing Fixtures | R | R | |
| WC Credit 1 | Landscape Design | 2 | 2 | |
| WC Credit 2 | Management of Irrigation Systems | 1 | 1 | |
| WC Credit 3 | Rainwater Harvesting, Roof & Non-roof | 4 | 4 | |
| WC Credit 4 | Water Efficient Plumbing Fixtures | 5 | 5 | |
| WC Credit 5 | Wastewater Treatment and Reuse | 5 | 5 | |
| WC Credit 6 | Water Metering | 1 | 2 | |
Certification Compliance Requirements:
- Design a rainwater harvesting system to capture at least ‘one-day rainfall’.
- Use efficient water-efficient plumbing fixtures that meet baseline criteria.
4. Energy Efficiency (EE): 28%
Energy consumption is an essential element in development. To reduce the overall energy consumption and increase on-site energy generation, here are the requirements:
| Module | Points | |||
| Owner-Occupied Building | Tenant-Occupied Building | |||
| Energy Efficiency(EE) | 28 | 30 | ||
| EE Mandatory Requirement 1 | Ozone Depleting Substances | R | R | |
| EE Mandatory Requirement 2 | Minimum Energy Efficiency | R | R | |
| EE Mandatory Requirement 3 | Commissioning Plan for Building Equipment & Systems | R | R | |
| EE Credit 1 | Eco-friendly Refrigerants | 1 | 1 | |
| EE Credit 2 | Enhanced Energy Efficiency | 15 | 15 | |
| EE Credit 3 | On-site Renewable Energy | 6 | 8 | |
| EE Credit 4 | Off-site Renewable Energy | 2 | 2 | |
| EE Credit 5 | Commissioning, Post-installation of Equipment & Systems | 2 | 2 | |
| EE Credit 6 | Energy Metering and Management | 2 | 2 | |
Certification Compliance Requirements:
- Encourage the use of eco-friendly refrigerants and halons in the building’s HVAC system.
- Design the building according to ECBC guidelines or ASHRAE Standard 90.1-2010 (Whole Building Simulation).
- Ensure all the building equipment and systems are in place to achieve high performance.
5. Building Materials & Resources (BMR): 16%
Green buildings are optimized with efficient segregation of domestic and hazardous wastes. It also features on-site waste treatment for reuse. The material selection includes local availability, reducing transport emissions, and durable and recyclable potential.
| Module | Points | |||
| Owner-Occupied Building | Tenant-Occupied Building | |||
| Building Materials & Resources (BMR) | 16 | 16 | ||
| BMR Mandatory Requirement 1 | Segregation of Waste, Post-Occupancy | R | R | |
| BMR Credit 1 | Sustainable Building Materials | 8 | 8 | |
| BMR Credit 2 | Organic Waste Management, Post-occupancy | 2 | 2 | |
| BMR Credit 3 | Handling of Waste Materials During Construction | 1 | 1 | |
| BMR Credit 4 | Use of Certified Green Building Materials, Products, and Equipment | 5 | 5 | |
Certification Compliance Requirements:
- Provide dry and waste bins within the facility.
- Segregate hazardous waste in a separate bin.
- Reduce building materials associated with negative environmental impact.
- Install an on-site waste treatment setup to treat maximum kitchen waste.
- Demonstrate 75% of reused or recycled construction waste instead of landfilling.
- Ensure that the project uses approved products of CII.
6. Indoor Environmental Quality(IEQ): 12%
This criteria consists of 12 points for owner-occupied buildings and 9 points for tenant-occupied buildings, out of a total of 100 points. There are 10 conditions derived under IEQ, including 2 mandatory requirements and 8 additional IEQ credits. The overall requirements are:
| Module | Points | |||
| Owner-Occupied Building | Tenant-Occupied Building | |||
| Indoor Environmental Quality(IEQ) | 12 | 9 | ||
| IEQ Mandatory Requirement 1 | Minimum Fresh Air Ventilation | R | R | |
| IEQ Mandatory Requirement 2 | Tobacco Smoke Control | R | R | |
| IEQ Credit 1 | CO2 Monitoring | 1 | 1 | |
| IEQ Credit 2 | Daylighting | 2 | 2 | |
| IEQ Credit 3 | Outdoor Views | 1 | 1 | |
| IEQ Credit 4 | Minimise Indoor and Outdoor Pollutants | 1 | 1 | |
| IEQ Credit 5 | Low-emitting Materials | 3 | 3 | |
| IEQ Credit 6 | Occupant Well-being Facilities | 1 | – | |
| IEQ Credit 7 | Indoor Air Quality Testing, After Construction and Before Occupancy | 2 | – | |
| IEQ Credit 8 | Indoor Air Quality Management, During Construction | 1 | 1 | |
Certification Compliance Requirements:
- Demonstrate that all regularly occupied spaces achieve minimum ventilation rates according to ASHRAE Standard 62.1-2010 for fresh air ventilation.
- Provide operable windows or doors to the exteriors in all regularly occupied spaces.
- Demonstrate that smoking is prohibited in the project by regulations set by the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India.
- Demonstrate that designated outdoor smoking areas are 7.6 m from non-smoking areas.
- Install CO2 sensors in return air ducts to ensure the CO2 level difference in regularly occupied areas does not exceed 530 ppm.
- Simulate daylight conditions on Sep. 21 at noon to ensure 75% of regularly occupied spaces achieve 110 to 2200 lux illuminance levels.
- Ensure at least 75% of frequently occupied spaces have a direct line of sight to vision glazing 0.9m to 2.1m high.
- Develop and implement an IEQ management plan following the ‘During Construction IAQ Management Guidelines’ from NBC Part 7.
7. Innovation and Development: 7%
The environment provides everything that human beings need. Creativity should be redefined to encompass the creation of new and innovative ideas. However, true innovation requires rigorous research and methodical approaches to ensure that new developments are scientifically meaningful. It is important to acknowledge that such efforts and their successful implementation deserve recognition. Here are the optional credits for innovation in architecture:
| Module | Points | |||
| Owner-Occupied Building | Tenant-Occupied Building | |||
| Innovation and Development(ID) | 7 | 7 | ||
| ID Credit 1 | Innovation in the Design Process | 4 | 4 | |
| ID Credit 2 | Optimization in Structural Design | 1 | 1 | |
| ID Credit 3 | Waste Water Reuse, During Construction | 1 | 1 | |
| ID Credit 4 | IGBC Accredited Professional | 1 | 1 | |
Certification Compliance Requirements:
- Show how the design process will document the intended innovation to validate its integration and application.
How to Become An IGBC Accredited Professional
The Indian Green Building Council (IGBC) encourages architects and other eligible graduates to practice in green building projects. Under IGBC credentials, you can find four different recognitions based on work experience, qualification, and levels of examination.

To become an IGBC-recognized green professional, carefully note down the following points:
a) IGBC AP-Professional:
Any professionals who have worked in the building sector for at least two years qualify to take this exam. If eligible, apply for the IGBC AP Exam. Click here to learn more about the examination.
b) IGBC AP-Associates-Students:
- Should have undergone an IGBC certification course online.
- Students or young professionals who have worked in the building sector for less than two years.
- If eligible, apply for the IGBC AP Associate Exam. Click here to learn more about the examination.
c) IGBC AF for Faculty:
All faculty members who have worked in the academic institution for at least two years qualify to take this exam. If eligible, apply for the IGBC AF-Faculty Exam. Click here to learn more about the examination.
d) IGBC CP for LCA Buildings:
- Enroll in the IGBC Certification Course.
- If you’re interested in working on life cycle assessments for green projects, register for the examination as part of the course. Click here to learn more about the examination.
Fees Structure:
IGBC charges different members to register and start the certification process, based on the membership category. The certification fee varies based on the square meter of the project. Parking area is not counted in the overall built-up area.
Registration Fees(INR):
| Membership Category | Fee(INR) |
| IGBC Founding Member | 25,000 |
| IGBC Annual Member | 25,000 |
| Non-Member | 30,000 |
Pre-certification Fee(INR):
| Membership Category | Base Fee | Additional fee for Projects with multiple buildings including common basements | ||
| 20k sq.m & below | >20k to 50k sq.m | >50k sq.m & above | For each additional building with a built-up area of 5,001 sqm and above | |
| Flat Fee | Flat Fee | Flat Fee | Flat Fee | |
| IGBC Founding Member | 2,00,000 | 2,50,000 | 3,00,000 | 50,0000 |
| IGBC Annual Member | 2,25,000 | 2,75,000 | 3,25,000 | 50,000 |
| Non-Member | 2,50,000 | 3,00,000 | 3,50,000 | 50,000 |
Certification Fee(INR):
| Membership Category | Base Fee | Additional fee for Projects with multiple buildings including common basements | |||
| <=5k sqm | 5k to 20k sqm | >20k to 50k sq.m | >=50k sq.m | For each additional building with a built-up area of 5,001 sqm and above | |
| Flat Fee | Based on sq.m | Based on sq.m | Flat Fee | Flat Fee | |
| IGBC Founding Member | 1,80,000 | 2,15,000 + 11.25 per additional sq.m | 4,25,000 + 11.25 per additional sq.m | 8,25,000 | 50,000 |
| IGBC Annual Member | 1,90,000 | 2,30,000 + 11.50 per additional sq.m | 4,40,000 + 11.25 per additional sq.m | 8,40,000 | 50,000 |
| Non-Member | 2,00,000 | 2,40,000 + 11.50 per additional sq.m | 4,50,000 + 11.25 per additional sq.m | 8,50,000 | 50,000 |
Choose a Project Category:
IGBC-recognized professionals can begin working on green building projects. However, every architect should carefully categorize their project and understand the appropriate criteria and compliance requirements. The IGBC categories are:
a) IGBC Residential
| IGBC Green Residential | |||
| IGBC Green Homes | IGBC Affordable Housing | IGBC Green Residential Societies | IGBC Nest |
b) IGBC Green Commercial:
| IGBC Green Commercial | |||
| IGBC Green New Buildings | IGBC Green Existing Buildings | IGBC Green Interiors | IGBC Green Healthcare |
| IGBC Health & Well-being | IGBC Green Service Buildings | IGBC Green Resorts | |
c) IGBC Green Industrial:
| IGBC Green Industrial | |||
| IGBC Green Factory Buildings | IGBC Green Logistics Parks and Warehouses | ||
d) IGBC Green Built Environment:
| IGBC Green Built Environment | |||
| IGBC Green Townships | IGBC Green Cities | IGBC Green Existing Cities | IGBC Green Hill Habitat |
| IGBC Green Mass Rapid Transit System | IGBC Green Existing Mass Rapid Transit System | IGBC Green Railway Stations | IGBC Green High-Speed Rail |
| IGBC Green Landscapes | IGBC Green Villages | ||
e) IGBC Net Zero
| IGBC Net Zero | |||
| IGBC Net Zero Energy Buildings | IGBC Net Zero Water Buildings | IGBC Net Zero Waste Rating System | IGBC Net Zero Carbon Guidelines |
f) Other Typologies:
| Other Typologies | |||
| IGBC Green Schools | IGBC Green Campus | IGBC Green Place of Worship | |
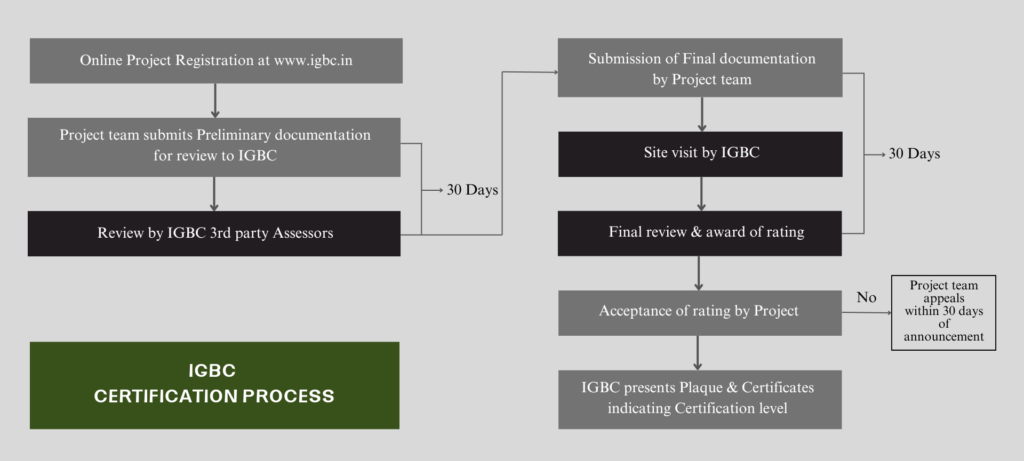
Steps to Achieve IGBC Certification
To accomplish this, the project owners should submit all the necessary documents and details to satisfy mandatory and credit requirements. The project submission requires the following:
- Project Brief
- General Drawings in the prescribed format
- Filled-in Templates
- Narratives and Supporting Documents
The above-mentioned requirements are assessed in the preliminary and final phases.
To conclude, should IGBC certification be the benchmark for sustainable green building projects in India? Complying with IGBC certification not only reduces the negative impact on the environment but also improves occupant comfort. This also reduces sick-building syndrome conditions and promotes health and well-being.
Having an IGBC certification and rating system as a tool should not limit the architectural and contextual design thought process of an architect. This checklist should enhance the aim of an architect beyond meeting the minimum criteria.
Content Writing And Research By: Ar. Baarat Krishna
